The current industrial regulations require parts to have clearly legible identifications, therefore, increasing the popularity of the laser marking process. Previous industrial trends required manufacturers to mark surfaces with traditional engraving or screen-printing processes. These processes were non-permanent, costly, and usually caused part defects.
Laser marking involves transferring a permanent mark onto a surface using a concentrated beam of light. Typically performed with a fiber, pulsed, continuous wave, green, or UV laser machine, laser marking encompasses a wide variety of applications.
Nowadays, laser marking has become increasingly important in the medical device industry. With manufacturers worldwide producing a wide range of medical devices, it is necessary to clearly identify the raw materials, instructions for use, risks and troubleshooting options. Medical professionals must have instantaneous access to the manufacturer and the product information in the event of a malfunction of an implanted device such as a pacemaker or cardioverter defibrillator.
With modern medicine, laser marking has expanded to include things like artificial joints, metal bone replacement plates, and screws that hold them in place. To ensure that the laser markings would withstand years of regular sterilization and use, they had to be durable and carry out without damaging the chemical passivation or corrosion-resistant coating.
Laser marking has no alternate in permanent marking when it comes for medical devices that goes under repeated passivation. Mostly medical devices and surgical tools are made of stainless steel 304-316 or titanium. These materials consist of chromium oxide (corrosion-resistant layer) on its surface. A laser mark visually contrasts with the natural colour of the alloy to make the mark visible – the purpose of the mark. The style of mark required by the medical device industry is called a “dark or annealed mark”. This mark does not remove any material from the part and so avoids any potential for any contamination to collect. Standard fiber- lasers or picosecond laser can produce such type of dark marks. These dark mark from lasers are desirable as they are visible from all the angles. Laser marks are also precise and passivation resistance.
A variety of optimized marking solutions are available from Coherent, ranging from laser marking subsystems for simple and complex applications to fully automated systems, such as our ExactMark series, that offer unattended operation on batches of identical devices accompanied by serial numbers. In this article, we’ll take a closer look at a few of the laser marking techniques.
ULTRAVIOLET (UV) MARKING OF PLASTICS
UV (ultraviolet) lasers Marking, Unique and premium laser Marker and engraver. This UV marking Laser is also called ‘Cold marking’. Ultraviolet lasers are ideal for most of these marking tasks since the high-energy photons from these lasers directly break the molecular bonds in plastic polymers. This can be used to cause a photochemical transformation that changes the colour of the plastic, without removing material or causing any thermal damage to the surface.
The most common photochemical transformation is to bleach a coloured material and leave a pale mark. Some materials are designed to produce other types of colour change. For example, ultraviolet lasers can create dark, high-contrast marks on nylon and polyurethane that are white due to titanium dioxide doping, as in nylon circuit breakers for residential use. Ultraviolet lasers can also mark transparent and coated, coloured plastics as well as performing cold engraving of coated and uncoated glass. In pharmaceuticals, UV laser marking is also well-suited to marking gel capsules and blister packages, and for creating QR codes on bottle caps.
Coherent is a world leader in pulsed ultraviolet lasers for marking and other industrial applications. Our decades of experience in ultraviolet applications deliver lasers with the highest reliability and longest lifetime, e.g., the PowerLine E 8 QT.
MARKING TUBULAR METAL DEVICES
Medical devices come in all kinds of shapes and sizes, but many have a tubular shape. So Coherent makes a fully automated laser marking machine just for this application, called AutoTube Marker. The operator places a batch of parts in the input bin and scans the data code. The machine then takes over and not only rotates and marks the parts as needed, it also scans the marked parts for user-specified pass/fail standards. And just as important, it creates a full data log for tracking and certification needs. Since it’s optimized for metal devices, AutoTube Marker comes with a choice of a traditional infrared laser or an ultrashort pulse (USP) laser such as our Rapid series which enables laser black marking.
LASER BLACK MARKING
In laser black marking a USP laser causes a nanostructuring of the metal surface which then traps light; the marked surface can appear quite black but without any chemical change or oxidation. Black marking is great for both aluminum and stainless steel. And the steel stays rust-resistant even after repeated sterilization (with steam.) You can read more about laser black marking here.
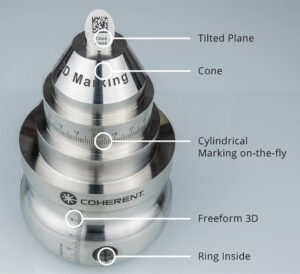
3D MARKING
So, a lot of medical devices are tubular and a few are flat, but some are neither; they can have sloping, curved, or unusually shaped surfaces that need to be marked on. For many years the only way to mark these surfaces with a laser was to resort to robotics or 5-axis CNC machines. Instead, Coherent provides a “smart” 3D marking solution that combines an extremely dynamic 3D focusing technology with novel 3D machine vision and powerful marking software called Visual Laser Marker (VLM). It visualizes the relative position of the laser and workpiece and provides an accurate preview of the marked part. The VLM software also accepts CAD design files of the workpiece, supports different 2D → 3D mapping types, and adjusts the marking process to free-form surfaces automatically.